Software testing best practices must be used when products are updated constantly to improve their performance and functionalities. Software testing has been imperative not only during the first development phase but also throughout maintenance. Therefore, your team needs a proper testing strategy that works in all circumstances.
Thus, we need to follow software testing best practices to make Quality Assurance effective. There are many advantages to QA. Some of them are creating quality products, reducing costs, increasing end users’ satisfaction, and improving the security of the final product.
In this article, we will discuss the best practices your team can follow during the four levels of software testing.
Plan Quality Assurance (QA) testing and processes
Creating a proper test plan helps the software teams communicate quickly. It will include all the procedures used for software testing purposes. As a result, the document benefits the new testers who join the testing team to better understand product objectives.
QA tests and their correlated tasks must be carefully planned initially. This helps us to outline terms and objectives while generating robust testing documentation. Besides, the QA testing methodologies offer the design and development teams the details to build a quality application.
Software QA does not rely on testing. Instead, it relies on the results of the tests. It is mandatory to adopt the QA testing approach according to the product the team is developing.
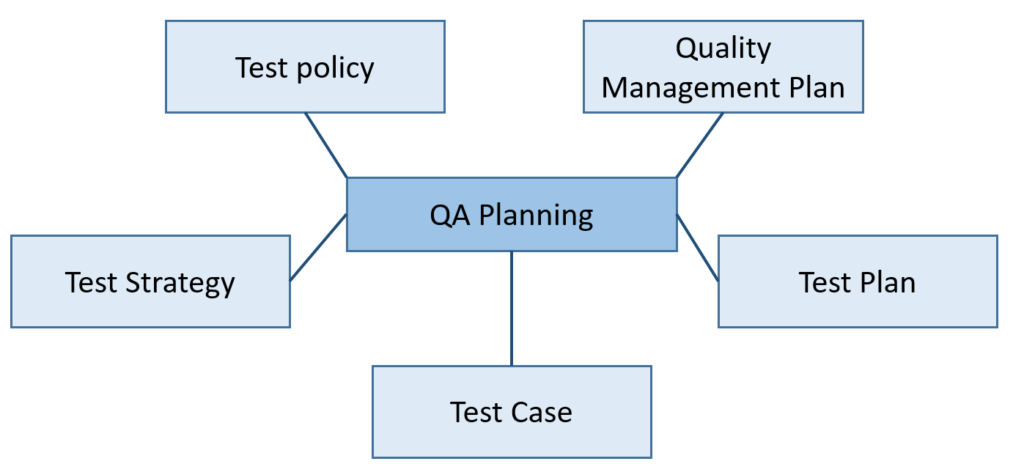
Components of a Quality Assurance (QA) plan
- Test policy describes the organization’s selected and approved test principles and primary objectives.
- Quality Management Plan includes software quality requirements. It defines the adequate level of quality targeted.
- Test Strategy is a high-level document that aims at the application’s business requirements.
- Test Plan is an operational document that detects the testing realm and other correlated tasks.
- Test Case defines the activities or set of requirements to test.

Integrate all Quality Assurance (QA) tests with the CI/CD pipeline
The software testing process will be successful if you test the development code as the existing code is modified. The QA processes we plan to execute must be automated within the CI setup to quickly test existing code. As a result, when the development code changes, it will pass through a test before the changes deploy to production.
Why is it essential to integrate Quality Assurance (QA) tests with the CI/CD pipeline?
As part of the CI/CD setup, using test automation is one of the industry-standard software testing best practices to deploy code to the production system without bugs and faults.
Consequently, each code must be automatically tested within the CI pipeline to acquire the best outcome from the development phase. Furthermore, testing within automated CI/CD pipelines improves the product’s security by discovering issues quickly.
Steps to follow when integrating quality assurance (QA) tests with the CI/CD pipeline
- Select the project’s appropriate CI/CD tool (e.g., Jenkins, Circle CI, Travis CI, etc.).
- Document the CI/CD pipeline components and elements.
- Use an efficient testing workflow with the test automation tool.
- Recognize the processes that can and should be automated.
- Recognize vulnerable points that result in crackups.
- Improve the collaboration among software developers and the QA teams.


Generate Reports from Tests
Among the best practices for software testing is generating reports. The main reason why you need to generate reports is to know whether the tests are successful. Apart from the software developers and software test teams, even the stakeholders will use these test reports to verify the status of the application.
We use these generated reports to log all the information related to the testing tasks and their frameworks. In other words, we need to log all the testing modules and their outcomes.
How to generate a beneficial test report?
- Include the results of all the test modules.
- Add a separate section to record the bugs.
- Explain the nature and behavior of the bugs, together with the frequency of their occurrence.
- Come up with solutions for the recorded bugs.
- Reproduce a bug before reporting it and include the steps for it.
- Include screenshots as evidence of the existing defects and bugs.
- Include a bug summary to quickly discover the nature and state of the bug/fault.
- Integrate the report with a bug-tracking system.
Test Early and Test Often with a Shift-left approach
Initiating QA activities at the start of development is one of the best practices for software testing, as it yields optimal results. Focusing on testing throughout the SDLC allows more realistic expectations to be set about deadlines without sacrificing product quality.
Shift-Left Testing
Traditionally, testing began after the completion of the development. However, the agile methodology requires testers to begin testing from the start of the project. By doing so, you uncover defects earlier by commencing testing earlier in the software development. As we all know, the earlier you find a bug, the earlier you can fix it. Thus, it saves you time and money and maintains positive team relationships. In addition, it accelerates product delivery and boosts coverage of tests.
Continuous Testing
Teams that implement Continuous Testing end up executing tests as a part of the delivery pipeline. Therefore, potential defect feedback is obtained faster, leading to more frequent releases.
Shift-Left Continuous Testing
Combining both Shift-Left and Continuous Testing principles yields Shift-Left Continuous Testing. The primary goal is to:
- Automate our product to the best of our abilities.
- Boost coverage of tests as much as possible.
- Run all tests in the development pipeline immediately.
Run Frequent QA Technical Reviews
Formal reviews of a technical nature are helpful because they uncover logical or functional errors in code, especially during the early stages of the SDLC.
Logical errors are caused by a defect and result in functionality behaving wrongly. A logical error does not cause the application to crash or terminate unexpectedly. On the other hand, functional errors happen when subpar exception handling breaks referential transparency.
Technical Reviews
These reviews are in a formal setting, such as a group meeting. Typically, stakeholders with varying roles establish the application meets standards and requirements.
These meetings are called “formal technical reviews,” or FTR. An FTR is commonly performed on mature applications where market segmentation and target users are already entrenched.
Reports are generated as outputs from the FTR. These reports answer the following questions:
- What was reviewed?
- Who was involved in the review?
- What were the findings of the review?
- What decisions were made?
There are three primary methods of review:
Review Meeting
The product’s author conducts the review and introduces the solution to the panel of other reviewers. Feedback on potential changes is received, and release timelines are discussed.
Walkthrough
A meeting is called to review the source code in an attempt to find defects and more efficient ways of coding and observe the documentation.
Inspection
Inspections are held to expand the initial standard and identify if defects found earlier are still reproducible.
Create a separate Software Team for testing
Some companies expect developers to do QA testing. But software quality control is a field that requires a different skillset from development. Also, developers won’t like to see bugs in their codes. Hence they could ignore some of the bugs they find or deliberately do a lousy job testing.
Therefore every company should have a QA team of software testers, which eventually leads to building a Testing Center of Excellence.
The main task of the team members in testing for software is to look for software bugs. They are responsible for planning tests, writing test cases, executing tests, etc. Much of the test documentation is held in software Test Management Software. In addition, if they find any bugs within the code, they are in charge of documenting and reporting them to the developers. As you can see, the duties of each QA role are vast.
Always keep this in mind to avoid ineffective software development, increased financial losses, and customer dissatisfaction:
Having a separate testing team can avoid incorrectly written software tests. This will allow the programmers to focus on the development tasks and let the testers do their job effectively.
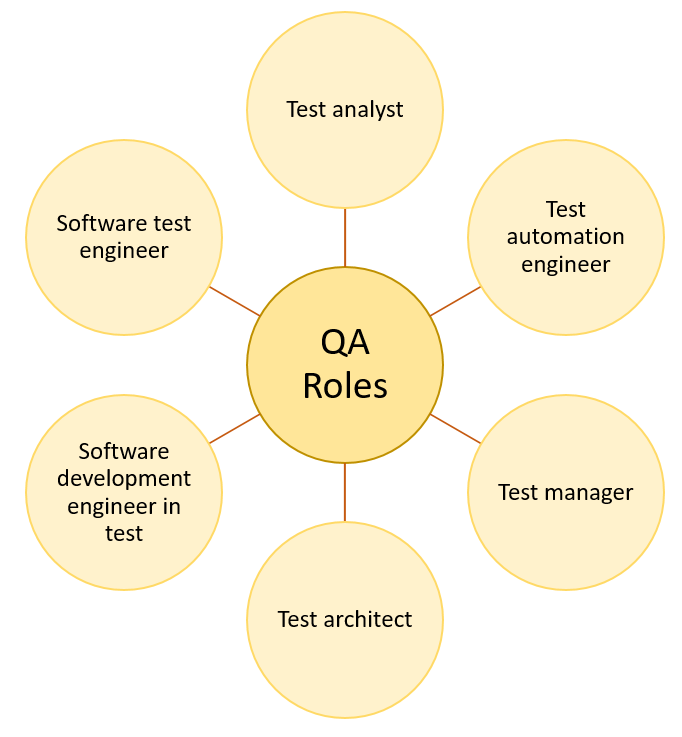
What are the primary Quality Assurance (QA) roles?
Let us look at the primary QA roles that contribute to the success of software testing.
- Software test engineer
- QA Engineer
- Test analyst
- Test automation engineer
- Software development engineer in test
- QA Specialist
- Test architect
- Test manager/QA Team Leader

What skills should a software tester have in general?
They must have strong skills in a variety of categories. A software tester needs to be able to suggest creative solutions and be fully aware of the best agile software testing practices, which can help identify any unusual or unexpected errors. They must also be patient and able to handle a high workload, as testing is arduous.
Write Tests for Maximum Coverage
We should write all types of tests covering most of the software’s functionalities. In addition, it is better to include all the valid/predicted conditions and unpredicted conditions for the test cases. This will test each functionality of the software against all possible outcomes.
Writing tests for maximum coverage will assist your QA team in recognizing the gaps in QA testing. As a result, you will be aware of the software components in your application that lack test coverage. Moreover, it evaluates the standard of existing tests and figures out useless test cases.
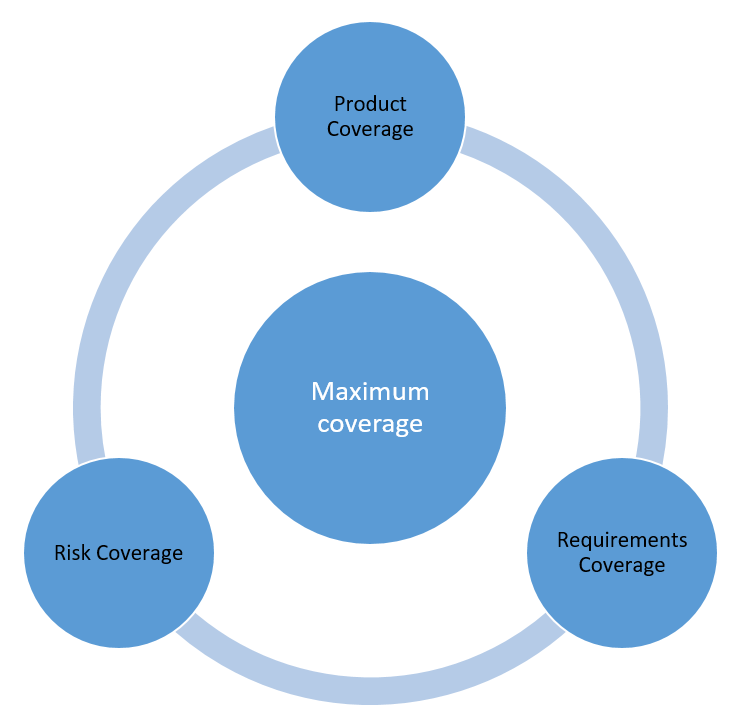
How to gain maximum coverage?
Maximum test coverage is gained through the following:
- Product Coverage helps your QA team verify the functions and features of the application are working as expected. In addition, it will guarantee non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, and availability.
- Risk Coverage assists us in evaluating the risks in the application.
- Requirements Coverage will outline the application’s business requirements and ensure tests cover them.
Optimize the use of Automated Tests
One of the QA best practices to enhance the quality of software applications is automating QA tests and using automation tools to execute the tests. This approach conserves time, lessens human errors, enhances coverage of tests, and performs batch testing together with parallel execution.
However, every test can’t be and shouldn’t be automated. Therefore, it is vital to understand when to use automated testing and when to use manual testing. The key advantage of automated testing is it can be integrated with Agile workflows easily. This is a healthy solution for companies moving fast towards Agile development. And it is important to keep in mind the software testing best practices before and during automation.
Following is a list of test automation tools:
- Selenium
- AccelaTest
- Katalon Studio
- Unified Functional Testing (UFT)
- Test Complete
- Watir


API automation can be extremely challenging for manual testers. AccelaTest empowers manual testers to create automated tests without requiring them to write a line of code.
Carry out Regression Tests
I would say this is the chief best practice among the practices in testing software. We use regression tests to guarantee existing features work fine even after modifying the application’s code. Regression tests must re-run the existing test cases and ensure they do not fail when we add a program or code modification. For that reason, performing regression testing would be helpful when there are requirement changes, and we wish to add a new feature to the software application. Furthermore, automated regression tests simplify and streamline the entire process, freeing the QA testers to focus on complex case-specific tests. Once automated, they can be activated by the code control system each time a build is formed.
What are the regression testing tools?
Following is a list of regression testing tools to automate the test cases and gain the maximum benefit of its reusability.
- AccelaTest
- Avo Assure
- Selenium
- Unified Functional Test/Quick Test Professional (UFT/QTP)
- Rational Functional Tester (RFT)


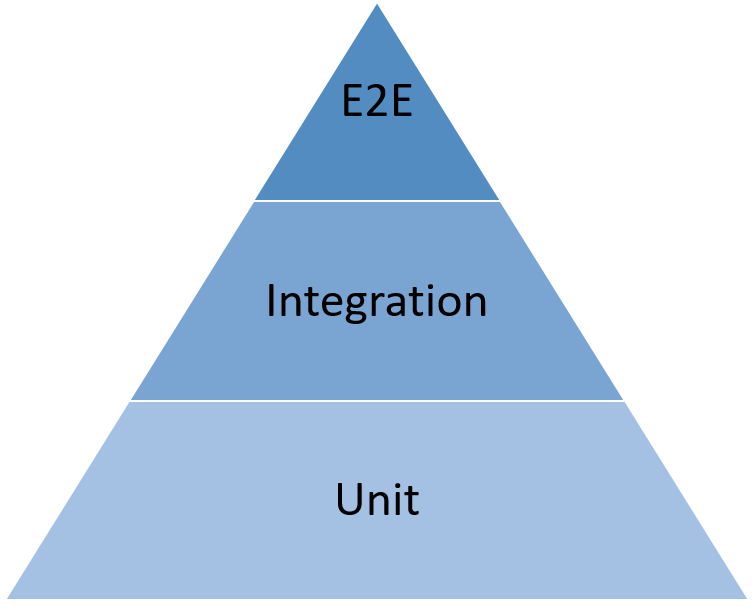
Rely on all levels of a Testing Pyramid
The Testing Pyramid is the basic framework that assists a software tester in accomplishing testing goals and building reliable test plans. The testing pyramid levels (E2E tests, Unit testing, and Integration tests) define the order and regularity of tests. The following figure is an image of the testing pyramid.

Benefits of relying on the testing pyramid
There are several benefits of relying on the testing pyramid. Some of the benefits are:
- Can streamline the testing process.
- Easy to carry out the tasks when introducing the testing requirements.
- Allows easy tests to execute in the very beginning. As a result, it enhances time management.
- Provides QA testers with the right priorities
- Gives the maximum test coverage.
- More suitable for agile processes due to its efficiency.
Create Testable Requirements
A development team’s dream is to have well-documented consumable and right-sized requirements. Conversely, their nightmare has obscure requirements that leave them scratching their head. How well functional requirements are written determines how testable they are and, ultimately, the number of resulting bugs.
When requirements are well-written, they adequately describe how the software feature behaves. Having good requirements leads to the ability to write tests that determine whether you meet each requirement condition.
To sum up, you should write the requirements in an active voice with clarity, completeness, and void of ambiguity.
Ideal Methods for Writing Requirements
There are numerous ways to write requirements that can lead to success. From traditional requirements to the more agile methods of TDD, BDD, ATDD, and User Stories.
Re-writing similar test cases, again and again, is a burden for a software tester. Similarly, writing the same codes in each test case is cumbersome. Even if the software testers manage to accomplish that task in the first place, they will face challenges when a requirement change appears.
Utilizing test design patterns and shared libraries will allow testers to minimize code duplication. As a result, software testers can manage their time while managing tests efficiently.
What are examples of test design patterns?
Following is a set of test design patterns popular among software testers.
- Page-Object Pattern
- Business-Layer Page-Object pattern
- Builder pattern
- Factory method pattern
- Lazy initialization pattern
- Singleton pattern can
- Adapter pattern
- Composite pattern
- Decorator pattern
- Façade pattern
- Iterator pattern
- Servant pattern
- Template method pattern
Follow the “green light” strategy and create backups
Even though we automate the tests for ease, we cannot ignore the possibility of such tests failing. Sometimes, these tests fail without indicating or letting the testers know. Or in some cases, these failing tests are ignored or removed without investigating further. As a result, errors in the testing pipeline will arise.
The “green light” approach can fix failing tests. Therefore, the testing pipeline will not encounter any errors, and the tests will produce the expected outcomes. The “green light” approach has the potential to resolve flaky tests that yield several results.
Our intention should not only be the passing of test cases. We must take the necessary steps to prepare for unexpected events, such as test crashes or cyber-attacks. Hence, one of the test-oriented development practices is getting regular backups of the data and other important testing-related things.
Rely Only on a Controlled Security Environment for Testing
Specifically, there is a high risk of getting caught with internet fraud and stolen data when a software tester works outside the secured office environment.
How to establish a secure environment to execute software tests?
- Avoid initiating connections with public networks – Connecting to a public network is unsafe as there is a high risk of an attack, putting the project and test data at risk. There will be an economic effect on the software company if the testers face an attack.
- Get to know who has access to your network – It is essential to know whether any other person has access to your network and who they are. If they do not belong to your software company, there is a chance that they will tend to steal data. To avoid this situation, we can provide access only to the testers of software and associated people.
- Enhance security awareness among the QA team – Knowing how to secure the testing environment will guarantee the execution of software tests in a controlled security environment. Following is a list of things testers of software can do to enhance the environment’s security.
- Email verification.
- Avoid clicking on unknown links and advertisement banners.
- Limit official data only to your work computer.
- Lock the computer when you are not using it.
- Avoid using personal accounts on work computers.
- Avoid using third-party software and update the software often – By making sure you are using only genuine software, you can minimize risks. Whenever a software product recognizes a vulnerability, the product owners fix the issues and release an update. The updated software will enhance the security of the test environment.
Maintaining a Dedicated Software Security Testing Team
Organizations with resources should establish a specialized software testing team to conduct rigorous penetration tests to ensure the highest levels of a secure testing environment. This will aid in finding and fixing any vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Concentrate on code changes and make use of code quality measurements
There are scenarios where software developers must modify the existing code. For example, if there is a requested requirement change, the developers will modify the code to fulfill the requirement. As a result, the test case written for the modified code set might not execute correctly and could fail. Hence it is essential to focus on the code changes and do the necessary modifications to the associated test cases.
Besides that, using code quality measurements will also allow us to get the maximum benefit of tests.
What are Software quality indicators and test metrics?
Even though there is no definite technique to estimate the code quality. We can use quality indicators and metrics below to get it done.
- Reliability
Reliability is one of the metrics we can use to know the duration an application can function without failure. The reason behind using reliability as a metric is to minimize application downtime. Reliability can be estimated by calculating the bug count in production. This can be achieved by reliability testing as well.
- Performance efficiency
We can utilize performance efficiency to be aware of the responsiveness of an application to perform an activity within a specific time duration.
The following measures are useful to estimate performance efficiency:
- Stress testing
- Soak testing
- Application performance monitoring

- Security
The capacity of an application to guard its data against dangers such as software breaches is known as Security. We can calculate the vulnerabilities count through security testing. This count will represent the security status of the application.
- Maintainability
Its maintainability is high if the software can transform, adapt, and re-adjust depending on its requirements. We can measure the maintainability of an application by calculating the number of code lines. The maintainability is low if the number of lines of code is high.
In addition, we can use complexity metrics such as cyclomatic complexity to estimate the complexity of the software. Know that the application is challenging to maintain when the complexity is high.
- Rate of Software Delivery
The Rate of Software Delivery is the only metric to know how often end users receive a software release or an update.

Break Tests in Small Fractions
One of the best ways to avoid complications and easily handle tests is by breaking them down into small fractions. Most of the major tests are complicated, with many lines of code.
Breaking down the tests into small chunks will help save time and resources when executing QA tests often throughout the software development life cycle. This testing process assists us in understanding each QA test individually. As a result, if a test fails, we are aware of the exact reason behind it.
For example, consider a scenario where we are testing an API’s GET, POST, and PUT endpoints. If we include all the tests into a single test and the test fails, it is difficult to understand the failure exactly and the related endpoint. But if we define three test cases for the three endpoints, we can eliminate this issue. However, depending on the test requirements and the application’s architecture, the breaking down of test scenarios will differ.
External library testing in Software Testing Best Practices
External libraries your project pulls in need thorough testing by their providers. Therefore you should not need to test the functionality of external libraries. However, you still need to perform integration testing on the libraries to ensure they integrate properly.
Form effective test strategies by understanding product objectives
The most effective testers bridge the gap between the technical and business perspectives. To successfully test a system, they must put end-users first and understand the user’s problem solved by the software.
When testers only focus on the requirements and lack business knowledge, they typically cannot see the forest for the trees. To successfully test the software, you must not have a narrow focus fixated on technical functionality.
Therefore, it is paramount to deeply understand how the whole product comes together to solve customer needs through its components, dependencies, integration points, and data flow.
Implement User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
Identify and create user personas for your software. These personas should be an approximation and target the optimal use of your software.
Personas are relevant for QA teams who use them as their guiding light as they navigate the system. They help the tester anticipate how a defect or functional error could trigger as they interact with the application.
However, having a user persona does not guarantee catching all bugs. Software testers cannot anticipate how an actual user will interact with the system as our users can be very unpredictable in their behavior patterns.
Therefore, bringing end-users to participate in the software development cycle testing is extremely important. User Acceptance Testing is typically performed during the last testing phase of an application. Reaching this important testing stage is a milestone and one of the final steps to the production release.
Our end-users observe a product through a different lens. As a tester who helps build a product from the ground up, you will have preconceived notions and intimate knowledge of how the system behaves. The end-user does not have the experience of testing a product every day, so each feature and response is novel to them. Thus, obtaining their unbiased product perspective is critical and one of the best practices for software testing.
There are Five types of UAT testing: Contract Acceptance Testing, Alpha and Beta Testing, Black Box Testing, Regulation Acceptance Testing, and Production Readiness Testing. By using these tests, actual software users can make informed decisions.
You cannot overstate the importance of User Acceptance Testing (UAT), as it is a critical step of the software development cycle. UAT helps to ensure that an application meets its end-user requirements by simulating real-world scenarios from the user’s perspective. Therefore, organizing UAT is equally important.
Implement exploratory and Ad hoc Testing
Automation testing can be a powerful tool, allowing developers to quickly analyze various aspects of their product. However, it still has limitations; automation is not enough to evaluate the user experience in detail. Consider other methods for obtaining meaningful and immediate feedback from the end-user’s perspective.
Exploratory and ad hoc testing exist to provide human creativity with a platform for finding defects that other, more structured tests may not uncover. These methods require minimal preparation or documents, often random in approach, as the tester discovers what works best during the discovery process. This way, you can increase testing coverage.
Test User Documentation
It is also important to ensure that it is easy for users to understand how the application works, and it should include screenshots and diagrams where needed. This is why user documentation (UD) is part of any software development process. This is a how-to manual or guide for using an application or service. It requires testing to ensure the documentation is up-to-date, accurate, and helpful. Test if any updates or changes in the application reflect in the accompanying documentation.
Carry out tests throughout the Software Development Cycle
Carrying out the testing processes only during the SDLC phase is not sufficient. It is mandatory to execute tests (especially unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests) for a better outcome from the testing processes. It is when a significant modification is done in the software development process or when you add or remove a new feature. Therefore, we need to plan the testing schedule at the beginning of the software development cycle.
Test-Driven Development (TDD)
In TDD, automated tests are created before any actual code for the application is developed. Every new feature begins with an automated test that fails.
The feature’s code is written after the test is created, ensuring the currently failing test passes. TDD boosts productivity and code quality, simplifies the code, and makes for better documentation.
Pair Programming
As with most things in life, two is better than one. Would you rather have two cookies or one? You can apply the same principle to testing scrutiny, a form of extreme programming. Two software engineers join one another to work collaboratively on a single computer. One engineer slings the code while the other makes suggestions and reviews.
A significant benefit of executing tests throughout the software development life cycle is detecting and identifying bugs and faults early as possible. As a result, we can enhance the quality of the software and reduce the number of defects in the final stages of the software development life cycle. This will also reduce the pressure on the software developers and build confidence among them to add required modifications to the application.
Increase the quality and speed
Gaining high quality and increased speed are the two main aims of any application regardless of the type of software, i.e., web application, downloadable software, or an API. When it comes to quality control of an application, we have to ensure that the efficiency of the QA process is high as we need to execute in different stages throughout the software development life cycle. This is why it’s essential for the QA team to follow software testing best practices to increase the speed of test cycles.
You can maintain the quality of the QA tests using test management systems. For example, if your team uses Jira, you need to use one of the best workflow management tools that fit Jira. In addition, it is essential to test the code written for automated tests to enhance the quality.
Managing quality objectives is also essential for faster market speed and higher quality. Ensure the goals align with the requirements of the end users. This will assist designers, software testers, and developers know the expected requirements.
Software Testing Best Practices Conclusion
Software testing is the process that we execute in the software development process to determine the performance of an application and discover whether the implemented software meets the requirements. In parallel, this process helps us to recognize the deficiencies and faults to guarantee the software product is defect-free to deliver a standard product.
Regardless of the testing method and the testing approach (manual testing or automated testing, white-box testing, or black-box testing) used, it is necessary to follow the QA best practices discussed above to get effective results from the software testing tasks.
